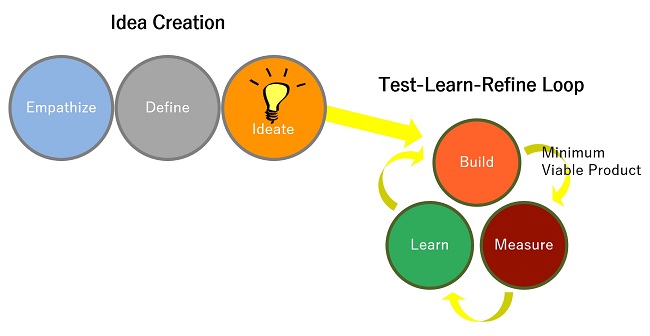
This is the complete scope of a new business strategy or new product development project from start to finish.
- For existing businesses or product concepts, we might engage only with the Test-Learn-Refine Loop to validate the current business or product vision and to provide any necessary refinements.
- For businesses in start-up or turnaround mode, we might start with the Idea Creation stage so that business strategy can be validated by consumer feedback to allow "failing fast" before significant investment of working capital.
- For new product or service concepts, our engagement could start either at the Idea Creation stage for early stage concepts that need refinement or the Test-Learn-Refine Loop to validate assumptions made in concept development and to gauge consumer or business acceptance.
Our Process Stages Defined:
- Empathize: Understand consumer/stakeholder/user needs. Gauge competitive environment. Gather market data.
- Define: Make sense of gathered data (qualitative & quantitative) and summarize design constraints for business strategy development or product/service concept creation.
- Ideate: Use gathered consumer/user/market insights to find solutions
- Build (Minimum Viable Product): In Lean UX terms, a Minimum Viable Product ('MVP') is the least amount of work needed to create something that can be tested for acceptance by the target market. In one famous example, Dropbox's MVP was a video of their file syncing process mocked up with images (no coding was done). Dropbox posted this video on their site to gauge user interest in their cloud storage/file syncing strategy after dozens of venture capitalists rejected their file syncing strategy as being a competitive advantage.
- Measure: Collect user feedback using the MVP. In Dropbox's case, their feedback was that 70,000+ potential users saw their MVP video on their Web site and signed up to get more information about their proposed but undeveloped product. User feedback at the Ideate stage can also include responses on how business strategies and product concepts might or might not fit user needs.
- Learn (and Iterate): Use the collected user feedback to determine what works and what does not with business strategies and product concepts to make them better. Repeat the Build stage and retest until user acceptance reaches desired levels.